To the page “Scientific works”
S. V. Zagraevsky
New researches of architectural monuments
of Alexandrov Sloboda
Published in Russian: Çàãðàåâñêèé Ñ.Â. Íîâûå èññëåäîâàíèÿ ïàìÿòíèêîâ àðõèòåêòóðû Àëåêñàíäðîâñêîé ñëîáîäû. M.: Àëåâ-Â, 2008. ISBN 5-94025-095-5
Chapter 1. The questions of the date of architectural monuments of Alexandrov Sloboda of XVI c.
Chapter 2. The reconstruction of Alexey Mitropolit Church
Chapter 3. A possible author of architectural monuments of Alexandrov Sloboda of 1510s
Chapter 4. The origin of hipped roof architecture
Part 1. W.W. Kawelmacher – the historian of architecture and restorer
Part 2. W.W. Kawelmacher’s bibliography
Part 3. A little about my father (memoirs about W.W. Kawelmacher)
Part 4. W.W. Kawelmacher’s obituary
Chapter 4.
The origin of hipped roof architecture
Attention!
The following text was translated from Russian original by the computer program
and has not yet been edited.
So it can be used only for general introduction.
1.
Questions of an origin of ancient stone tent-roofed architecture in the future we will call it the marquee architecture, material structures will specify only in the case of wooden architecture) occupy researchers is not the first hundred years. For a detailed historical overview of all points of view put forward beyond the scope of this study, only list the "basic" position (in chronological order of their appearance):
- hip architecture of Ancient Russia was a direct or indirect reminiscent of the late Gothic Western (Karamzin, Imoneynet, LDL, E.E. Golubinsky, A.I. Nekrasov, H. Wagner)1;
- hip architecture - a phenomenon that has been formed on the basis of old Russian wooden architecture (ia Zabelin, FF Gornostayev, Grabar, N. Voronin)2;
- hip architecture happened 3;
- hip architecture was formed under the influence of the architecture of ancient castle towers (PN Maksimov, mA Il'in, mn Tikhomirov, H. Wagner)4;
- by becoming a hip architecture greatly influenced by the ancient pillars of the Church-bell (mA Il'in, H. Wagner)5;
- old Russian pavilion was "an accident in the architecture and just replaced the dome, overlapping SPLA (Kavelmaher)6.
Before to start to address these hypotheses, we note that the revision of the position relative to the first ancient temple of hip and his architect (see 1 main and 3), cannot by itself significantly affect the choice of one or another point of view researchers or to develop a new theory of the origin of hip architecture: one of the Grand temple (ascension 1529-1532 period), with high probability, built by Italian architect (petroc minor), "replaced" by another (Trinity 1510-ies), and with high probability, built by Italian architect (Aleviz New). Both temples belong to the era of Basil III, marked by the flowering of architecture and the search for new forms.
The only thing we will further study the "replacement" of the Church of the ascension at Trinity Church - the traditional forms of the quadrangle of the latter.
And we start with a statement of fact that is hard to question, - that during the formation of the ancient Russian architecture of the XII-XV centuries, it is steadily growing "striving upward, characteristic of Romanesque and Gothic. General "high" proportion of temples7, the emergence of high arches, processing drums keel corbel arches8, the building above the domes high onion domes9 the construction of the column churches "under the bells"10- all of these phenomena are in line with overall impression "Lancet", which produces Gothic.
Characteristic of Gothic tendency to increase and zalnosti" the interior of the temples also reflected in the ancient Russian architecture - the pillars was getting thinner and thinner, smaller and smaller temples had inside shoulder, appeared pillarless temples " pylon11and then groin vault12. Assumption Cathedral Fioravanti, for example, S. pod'yapol'skii rightly belongs to the type of Gothic hall Church"13 and H. Wagner wrote that "if the development of "high-rise" architecture was not interrupted by the Mongol invasion, then Russia would have known something akin to Gothic14.
In this regard, we must assume that the emergence of "upward" hip architecture corresponds to one of the major trends of Gothic, and this is a serious argument in favor of the position nm Karamzin, im Snegireva, L.V. dal, E.E. Golubinsky and A.I. Nekrasov. Here we'll take and position Neemrana (temples with elevated supporting arches), Mailin, PN Maksimov, Mentionarea and Wagner (pillar-shaped temples and free-standing towers), as all this is, as rightly noted H. Wagner15, is closely associated with the "tall" Gothic features and, therefore, with a marquee architecture.
But the question arises: is connected directly or indirectly?
Here are a number of provisions that force us to deny a direct link hip architecture and Gothic.
First, higher arches and canopied temples are completely different constructive entity (arches supporting the dome, and the tent itself is in place supported by arches and domes), and have a direct parallel between them illegal.
Secondly, pillar-shaped temples before the erection in 1510-ies the Church of Metropolitan Alexei Alexandrov Sloboda and the Cathedral of St. Peter the Metropolitan of vysokopetrovsky monastery had not unlike tent churches, more or less extensive SPLA, i.e. from the point of view of their architecture were closer to the towers, than to the Church buildings (examples - Church-bell John Climacus 1329 and 1505-1508 years, Novgorod "chasozvonya" 1443, first of khutynsk pillar 1445).
Third, direct or indirect Parallels between the fortified towers and temples marquee void. The first had a very utilitarian character, the second appearance is determined primarily spiritual needs and architectural thought era. Moreover, from a utilitarian point of view tent churches had no sense, as compared to "scale" a cross churches (especially with the European basilicas) their area SPLA small, and "kolodtseobraznost" interior creates a lot of problems with acoustics.
Fourth, for the Western Gothic (like romanik, as for the Renaissance) is absolutely unusual overlap SPLA tent. Over sredokrestiyami sometimes were built or stone octahedral dome (Romanesque Cathedral in Speyer (Speyer) and Limburg Lana - Fig. 36)or wooden tents (Gothic Church of our lady in Bruges - Fig. 37). Sometimes decorative wooden tents were erected over the stone domes (Romanesque Cathedral in Padua, Fig. 38). Not one stone of the tent or on the naos or above the crossing in a more or less meaningful the temple we do not know. Tent complete the form used in the Romanesque-Gothic Europe in large numbers only for the towers.

Fig. 36. The dome above the crossing of the Romanesque Cathedral in Limburg on Lana.

Fig. 37. Gothic Church in Bruges.

Fig. 38. The Romanesque Cathedral in Padua. Above the Central dome was erected decorative tent.
This fully applies to the East, where, in addition to towers, stone tents sometimes overlap small mausoleums (as in the Volga Bulgaria).
In this connection it is necessary to make an important reservation: determining the origin of hip architecture and speaking of the first stone tent-roofed Church, we can not specify that we are talking about Ancient Russia. The other options here can not be, because the construction of large temples, stone covered with tents, unprecedented in the world had.
Acciona wrote that the alleged origin of hip architecture of Gothic "found in the source form of the tent, but not hip typology of the temple. This means that nothing was found: the architectural typology does not consist of individual parts on the principle of collage. If we assume that the Russian tent comes from the Gothic spire, we subsequently have to assume many intermediate links between the two typologies - Gothic bell tower integrated into the vaulted Basilica, and the Russian detached centric tent-roofed Church. For example, Russian Basilica with belfry, from which ZAT%DThe available evidence is insufficient. May not be such that the spire "cut down" from the bell tower and hoisted on the way undertaken (and, it appeared, by the way, nowhere) octagon on square"16. We must fully agree with the researcher.
Fifth, one of the most characteristic trends Gothic - increase the area of the internal space of the temples. With marquee same architecture, the situation is the opposite: we have already said that compared to "scale" a cross churches, and especially with the European basilicas, their area SPLA small.
Sixth, the beginning of XVI century in Italy was marked not Gothic, and Renaissance. And it is very unlikely that a highly qualified Italian architect of the time, whether New or Aleviz Petroc Small, could focus on the Gothic. As we know, the term "Gothic" Italians XV-XVI centuries, and means "the art of the willing", i.e. the "barbarians".
It is useful to note that in the Church of the ascension in Kolomenskoye, as shown by S. pod'yapol'skii, there were numerous "Renaissance" elements (orders, portals with direct architrave tie beams openings, "Renaissance" drawing Gothic visperhof etc). Against taking place in Kolomna temple Gothic elements (total stolpoobraznosti and many e%D17.
We can all agree with SS pod'yapol'skii and to say the same about Aleviz New: in the temple of Alexander the settlement contains many elements of the architecture of the Renaissance (decor, portals, colonnade, etc.) Orientation of Aleviz on Renaissance confirmed by the architecture of its first Moscow building - Arkhangelsk Cathedral. All "Gothic" elements in temples built by the Italian architect, are as petroc minor, stylized old Russian architecture (and St. Basil's Cathedral in Alexandrov Sloboda, as we have already noted, in General, is a direct remake of" the Trinity Cathedral of the Trinity-Sergius Lavra).
2.
Now we can proceed to the consideration of hypotheses regarding the origin of hip architecture of old Russian wooden architecture.
"The chronicler briefly the Russian land" (XVI century18) under the year 1532 says: "the great Prince Vasily placed the stone Church of Vnesenie of our Lord Jesus Christ up on the wooden case19. This message draws a direct parallel between the Kolomna temple and wooden architecture, and argue with that documentary evidence is hardly possible.
We have the image of unpreserved wooden tent-roofed Church in the village una Arkhangelsk region (Fig. 39), the construction of which registers the records referred to 150120, respectively, this Church was built before the first stone temple of hip.
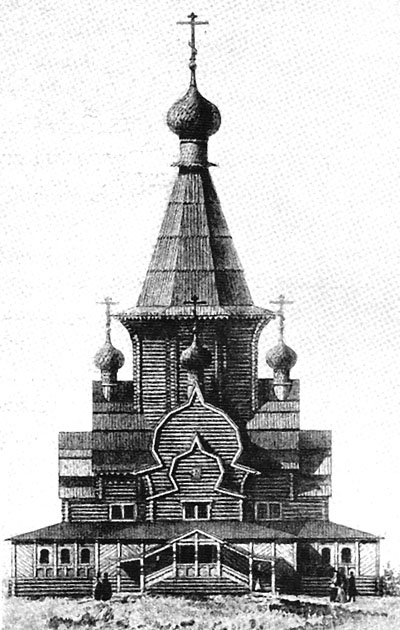

Fig. 39. Church in the village una Arkhangelsk region.
N.N. Voronin and PN Maksimov believed that the tent wooden Church was a common type of ancient Church in the pre-Mongolian time21and we can take a number of arguments in support of their position.
First, these researchers have provided examples of images wooden tent churches on the icon of the beginning of the XIV century from the village curve (Fig. 40) and on the margins of the Pskov handwritten "Charter"22.
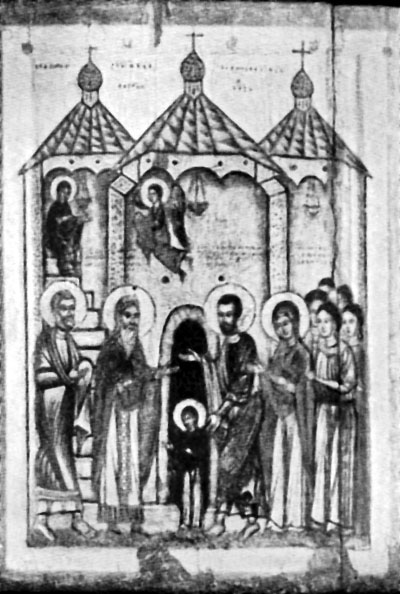

Fig. 40. The icon of the village of the curve.
Secondly, these researchers believed on the basis of textual and iconographic analysis of ancient documents that marquee were non-preserved wooden churches in Vyshgorod (1020-1026 years)23, Ustyug (end of XIII century)24, Ledsam graveyard (1456)25 and Vologda (the end of the XV century)26. About the Church 1501 in the village una we mentioned above.
Third, these researchers have led the chronicle reported high "stanah" in Moscow27 and showed that we are talking about a wooden tent pillar-shaped churches28;
Fourth, wooden belfry is shown in the image of the Tver Kremlin first half of the XV century on the icon Michael of Tver and Duchess Xenia29 (Fig. 41).

Fig. 41. The image of the Tver Kremlin first half of the XV century on the icon Michael of Tver and Duchess Xenia.
Fifthly, it is highly likely that many of the wooden tent-roofed temples of the XVI-XVII centuries are copies of more ancient. This position was justified Acciona30 on the basis of the following considerations:
- folk architecture conservative typology change very slowly;
- there was a practice to replace rotten logs in the frame of one, why time in the ancient monument of the original material could be very small. Therefore, radiocarbon Dating and dendrochronological method relatively reliable only if for analysis take a large number of logs. Accordingly, some wooden monuments due to a lack of representative sample material for analysis could receive a later date;
- carpenters are often obliged to build a new Church on the model of the old, dilapidated.
Sixth, wood is much easier to build a tent than the dome, and stone dome to build simpler than the tent. The reasons for this are the following:
- technology of building stone domes (and formwork, and without it31) was well known and established since the days of Ancient Rome;
- stone tent has almost the same rip as the dome, and to achieve uniformity of spreading at a high altitude tent (relatively speaking, to mean not "dipped") is a difficult engineering challenge;
- large stone tents before the beginning of the XVI century nowhere in the world was erected (very rarely built small tents over small churches, chapels, baptisteries, tombs, Breweries and kitchens32 - Fig. 42);
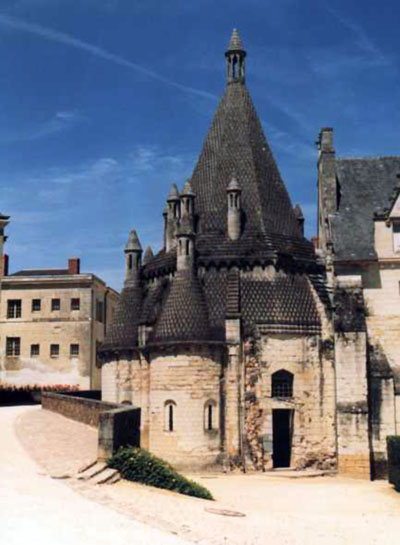

Fig. 42. Kitchen in the Abbey of Fontevraud (Romanesque).
- from wood to build the dome is very difficult (you will need to attach any logs semicircular shape, or use them very short intervals);
- the construction of wooden tent several (usually eight) logs - the edges of the tent - are reduced at the top and covered with boards, and it can make almost any little bit of a skilled carpenter. And not in vain, as we have noted previously, all known Gothic tents over sredokrestiyami - wooden.
That tent from wood to
build much easier than the dome, it follows that the tent could be
"simplified" dome during the whole time of existence of the old
Russian wooden architecture, including in the XI-XV
centuries. I can give an example of such replacement outside Russia - rotunda
over the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem, which until the nineteenth century were wooden.
P is
In this regard, it is appropriate to support the position Kavelmahera in that pavilion was simple replacement dome, overlapping SPLA, is the only significant caveat that this change in the wooden architecture was no accident, but the design-based phenomenon.
And because the tent in the wooden architecture was multi-faceted (this is due to the heart of its design - beams forming the frame), it is logical that the richness of acquired and drums. The number of faces more often equal to eight (apparently, this number optimally and to make the transition to the tent of Chetverikov, and for maximum stability of the structure). Thus, we see the source form "octagon on square".
Grabar and FF Gornostayev questioned the origin of the tent of wooden architecture, due to the fact that the tent end of the tree would have to focus on patterns in the stone, which until the XVI century was absent33. But in XI-XV centuries, wooden tents over the SPLA were quite clear samples - dome stone temples.
Another questioned the origin of the tent of wooden architecture may be due to the fact that preserved ancient wooden churches tent top is usually not closed down, and separated from the SPLA horizontal ceiling. But the reasons for erection of additional ceiling convincingly demonstrated Wagrain: it was caused by the need to protect the facility Church iconostasis from the rain and snow that falls in the gaps between the boards of Polis and timber fellings in strong wind; effective functioning of ventilation in the upper level of the log structure; independent stable ventilation in the%34. Known case of separation of the tent of downstream areas and stone architecture - the refectory Vvedenskaya Church of the Dormition monastery in Staritsa (1570).
GP Goltz believed that "vertically directed stone tent-roofed architecture may not occur on a horizontal directed wooden constructions"35. But there are many examples of vertical wooden churches (as already mentioned by us the Church in the village of Ura (Fig. 39), the Church of St. Elijah 1600 Vysokogo churchyard top-Tomskogo district, the Arkhangelsk region - Fig. 4336, Epiphany Church 1605 in the village of chelmuzhi Zaonezhie area of Karelia - Fig. 4437, Church of the ascension of 1654 in the village Pialy Onega district, the Arkhangelsk region - Fig. 4538 and mn. others), and the wooden tent (anyway, its frame) usually does not consist of horizontal and vertical logs.
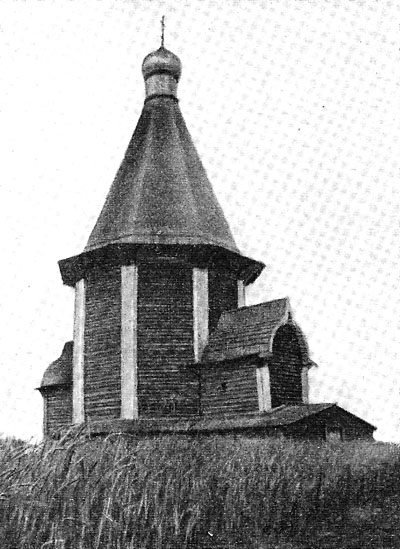

Fig. 43. The Church Vysokogo churchyard of the Arkhangelsk region.
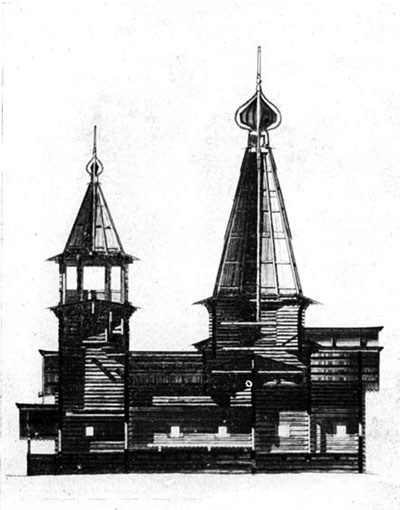

Ðèñ. 44. Öåðêîâü â äåðåâíå ×åëìóæè Çàîíåæñêîãî ðàéîíà Êàðåëèè. Ïðîäîëüíûé ðàçðåç.
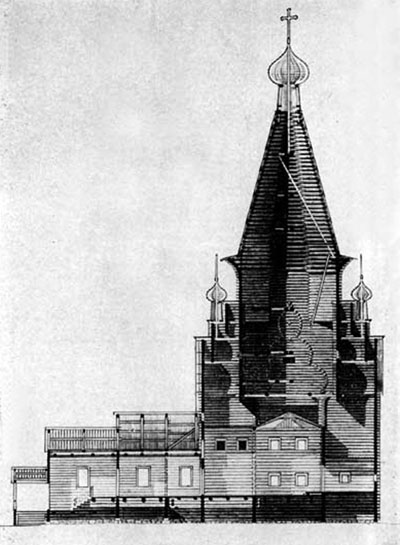
Ðèñ. 45. Öåðêîâü â ñåëå Ïèÿëû Àðõàíãåëüñêîé îáëàñòè. Ïðîäîëüíûé ðàçðåç.
But in this connection it is necessary to make one very important observation: in General, "vertically directed" wooden tent-roofed architecture generates no less "Gothic" Association than stone.
Of course, hardly rural (and urban), the carpenters were familiar with Western European experience, is probably Gothic "altitude" came in the wooden architecture indirectly (through the ancient stone pillars churches and temples with elevated supporting arches). But actually it does not change.
3.
We see a fairly extensive set of factors that were capable of directly or indirectly affect the appearance of hip architecture. All these factors have a very high cross-correlation, due to which any logical construction sooner or later "closed" to each other.
As an example, the basic postulates, the validity of which we have shown in this study:
- steepled churches are clearly typological relationship with pillar-shaped bell-towers and temples with elevated supporting arches;
- "high-rise" pillar-shaped temples "under the bells", as the temples with elevated supporting arches, appeared in Russia under the influence of late Romanesque and Gothic;
- for Gothic absolutely unusual overlap SPLA (and even sredokrestiya) tent, the more stone;
- hip architecture contradicts one of the main tendencies of Gothic - increase the area of internal space of the temples;
- Italian architects of the Renaissance could not directly focus on the Gothic style;
- in the work of Italian architects in Russia has been a conscious styling forms in accordance with local traditions;
- wooden tent-roofed architecture was extended to Russia before the XVI century;
- there chronicle proof of origin of the stone architecture of the wooden tent;
- wood is much easier to build a tent than the dome (a stone dome to build simpler than the tent);
- in the wooden architecture of the tent was the replacement of the dome, overlapping SPLA;
- General "high altitude" of ancient wooden churches were influenced by a stone pillar-shaped temples and shrines with elevated supporting arches;
- stone pillar-shaped temples and churches with elevated supporting arches, appeared in Russia under the influence of late Romanesque and Gothic.
"Logical circle has closed. In this case, the "closure" means that the emergence of hip architecture in varying degrees, affected all the above factors.
Therefore, each of the researchers, whose position we discussed in paragraph 1, was in his own right.
But out of loyalty to such a wide range of positions can be concluded: hip architecture has been prepared by the entire previous history and Russian and world architecture, with all the infinite set of relationships, influences and origins.
However, the construction of the first tent-roofed Church was brilliant creative breakthrough", and we can try to at least hypothetically reconstruct the specific circumstances of the appearance of the stone tent erected in the Church of the Trinity of the Alexander settlement under the project of the New Aleviz.
Theoretically, we can assume that the source of inspiration for the architect to have tents that housed the biblical patriarchs Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob. In the future, these pavilions became a symbol of the dwelling, i.e. the "porch", and the same value in the words of the prophet Isaiah received the sky: "He (God - SZ) stretches out the heavens like a curtain, and spreadeth them out as a tent to dwell in" (ISA. 40:22). MA Il'in, trying %39, îáðàòèë âíèìàíèå íà ýòè ñëîâà ïðîðîêà è íà èõ îñíîâàíèè ïðèäàâàë øàòðó «îñåíÿþùóþ» ðîëü40. But the researcher himself wrote that "the arches" is most fully expressed in the Church's cross (the dome on the pillars)41and it remains unclear, why in the XVI century, the architect decided to replace one "canopy" (dome) to another (tent). If a tent in the Church tradition had any independent symbolic (and even more canonical) value, it is as a phenomenon of stone temple architecture would have appeared much earlier than the beginning of the XVI century. And the prophet Isaiah, "tent" is a symbol of any home, absolutely optional tent-shaped form.
In accordance with the "Occam's razor" ("should not multiply entities beyond necessity"), we can assume that the source of inspiration for the New Aleviz were not rotunda over the Holy Sepulchre in distant Palestine and not abstract biblical characters, and specific the Grand order and surrounding architect of the old Russian architecture.
In Ancient Russia since the end in the mid - XII century playback of Byzantine models specificity ktitorskih orders given by invited foreign architects, was that the task was built not Italian, German or English churches, namely Russian. In other words, from architects have always wanted to work in line with the already established at the time of the traditions of Russian architecture, despite the fact that they were free to make the principles and elements of different styles, adopted in their country of origin.
From this General rule we do not know no exceptions. So, the construction of the "Western" the material is white stone - in the pre-Mongol Suzdal was conducted, including masters of Frederick Barbarossa, "Byzantine" (by that time already traditional for Ancient Russia) cross-forms, though with the introduction of a number of Romanesque elements of the decor and General "elevation"42. The construction of the pillar-like churches "under the bells" (probably the first of these was the octagonal Church of St. John Climacus 132943) was prepared four-column temples with high supporting arches and columns - " pylon44. The Church with groin vaults became a logical development of a four-column temples45. Octagonal Cathedral of St. Peter the Metropolitan (1514-1518 years) - a continuation of the tradition pillar-shaped temples "under the bells", although lacking the function of the bell tower. Assumption Cathedral in Moscow (1475-1479), the inner space of which is solved in the spirit of Gothic hall Church", and devoid of altar apse Trinity Church in Chashnikovo (XVI century) by architectural type are Klas is
In short, from the "mainstream" of ancient architecture not drop any Church, including built invited foreign architect. As we showed above, is no exception and tent architecture.
On this basis, we may assume that the New Aleviz received from the Grand Prince Basil III the task is to build a Palace-temple complex of Alexandrov Sloboda in "national" style - naturally, in the measure of understanding and perception of this style of famous European architect. Neither in Europe, nor anywhere else in the world was not such buildings as churches Settlement 1510 s - hence Aleviz took a sample architecture, surrounded him in Russia. Similarly, in due time the
However, the taking of a sample in no case did not mean a complete up - even Pokrovsky Cathedral in Alexandrov Sloboda, built on the direct sample of the Trinity Cathedral of the Trinity-Sergius Lavra, differ from the design type and proportions and size, and the decor, and the fact that it is built of bricks, instead of white stone, and the fact that its vertical wall (Trinity Cathedral they "pyramid" tilted inwards).
Therefore, Aleviz New built their churches in Russia as understanding of Russian architecture, and to apply the General volume-compositional and decorative solutions, which saw around himself, without abandoning their own creative search and the techniques of the Renaissance, which he had, as they say, "in the blood".
In this regard, we can assume that elevated Aleviz stone tent over the naos of the Trinity Cathedral in the Alexander settlement was built under the impression General elevation and "Lancet" Russian churches, including wood. The latter due to their huge number and formed the overall appearance of the ancient temple architecture is no less if not more, than the few temples, especially as the construction was not in the "white-stone" Moscow and in the province, Alexandrovskaya Sloboda. So, Kavelmaher wrote: "Among churches Sloboda only the Church of the Holy Trinity does not have the stone porch, as was originally built the wooden mansions... On the appointment of Trinity Church as the heart of a residential, wooden, intimate part of the Palace is also evidenced by its simplified, "prjamoslojnoj" "in the wooden case" architecture, in particular, such forms as exaggerated the police band tent, cornice without architrave and frieze, no capitals of the blades, "chapel-prirub" and she portals"46.
Thus, the use of Trinity Church instead of a dome tent, it may by Aleviz New intentional introduction into the stone architecture "Divadelni" motives that are organically linked in a single architectural ensemble of the stone temple of Alexander the settlement and mainly wooden (albeit with many stone houses47) Palace of Vasily III. However, there is another option: the task of the architect was the maximum diversity of four temples Sloboda 1510-ies, as with "normal" dome on a "normal" drum Trinity Church too would be like the neighboring Church of the assumption, and in this situation it was decided to use instead of a dome tent.
Of course, any reconstruction plan of the architect can only be hypothetical. But what hip architecture is an organic continuation of the preceding ancient architectural tradition, we may take for granted. And this tradition included and wooden architecture, and a wide range of relationships with the global architecture.
© Sergey Zagraevsky
Chapter 1. The questions of the date of architectural monuments of Alexandrov Sloboda of XVI c.
Chapter 2. The reconstruction of Alexey Mitropolit Church
Chapter 3. A possible author of architectural monuments of Alexandrov Sloboda of 1510s
Chapter 4. The origin of hipped roof architecture
Part 1. W.W. Kawelmacher – the historian of architecture and restorer
Part 2. W.W. Kawelmacher’s bibliography
Part 3. A little about my father (memoirs about W.W. Kawelmacher)
Part 4. W.W. Kawelmacher’s obituary
To the page “Scientific works”